Improve page load speed, reliability, and user experience with Aspirapps's globally distributed CDN.
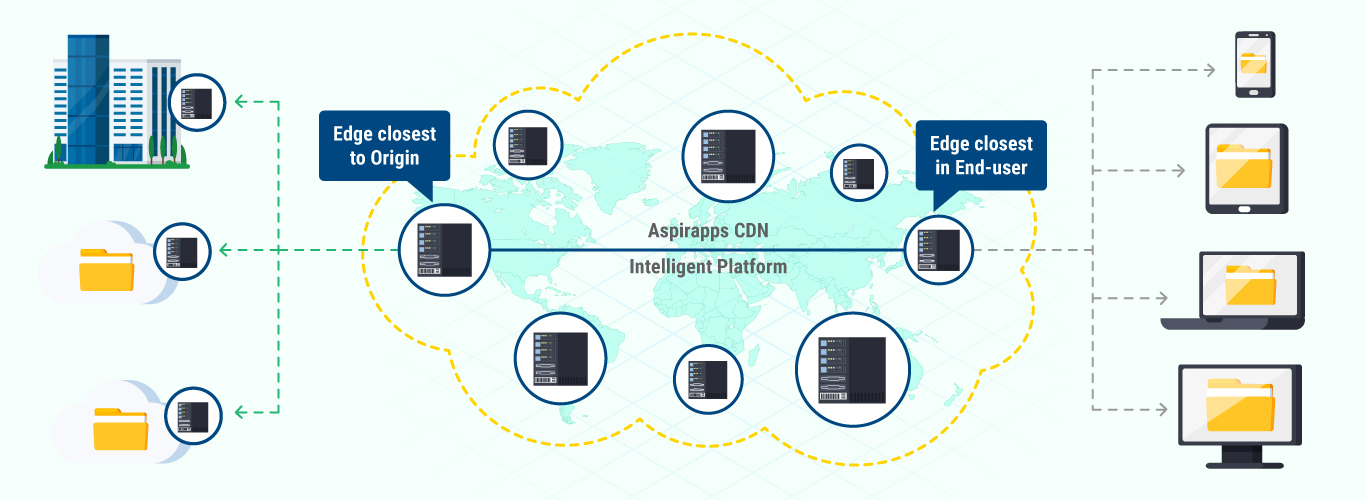
CDN is an umbrella term spanning different types of content delivery services:
If you’re in the stage where your website has started to grow and receive more traffic, it’s time to think about getting a CDN.
Because CDNs are placed closest to the user, it’s possible to reduce latency when the distance that your content needs to travel is shorter. A CDN can make your website load much faster. For example, if your website is based in the UK and you get traffic from the U.S., it’s possible that your CDN provider has a server in the U.S. and will use that server for your website.
A CDN can ensure that a network has a high data threshold. A large number of users can thus access the network at the same time without delays. By enabling a high traffic flow, CDN allows people from all over the world to access your website simultaneously.
Servers in the CDN are always running, and your website is accessible even if your server is down. Without a CDN, your server can sometimes be down which means that you have to wait until your host fixes the problem. This cannot happen if you’re using a CDN. In case of a crashed server, the CDN will use your cached pages.
The delivery of content is more consistent if you’re using a CDN. In particular, this concerns high-resolution content such as videos and images. CDNs provide high-quality content delivery and thus have a substantial impact on your website’s performance.
When a CDN monitors your asset delivery, operators can determine where extra capacity is needed, based on real-time statistics. If the server in a certain region is suffering from overload, operators can provide extra bandwidth to make sure that everything is running smoothly.
If your website suddenly experiences a large inflow of traffic, you can benefit from CDN services. A large network of servers ensures that these resources are available and scalable in all cases. It’s a nightmare of many businesses that they will get a major increase in traffic, but their website cannot handle it.
At its core, a CDN is a network of servers linked together with the goal of delivering content as quickly, cheaply, reliably, and securely as possible. In order to improve speed and connectivity, a CDN will place servers at the exchange points between different networks.
These Internet exchange points (IXPs) are the primary locations where different Internet providers connect in order to provide each other access to traffic originating on their different networks. By having a connection to these high speed and highly interconnected locations, a CDN provider is able to reduce costs and transit times in high speed data delivery.
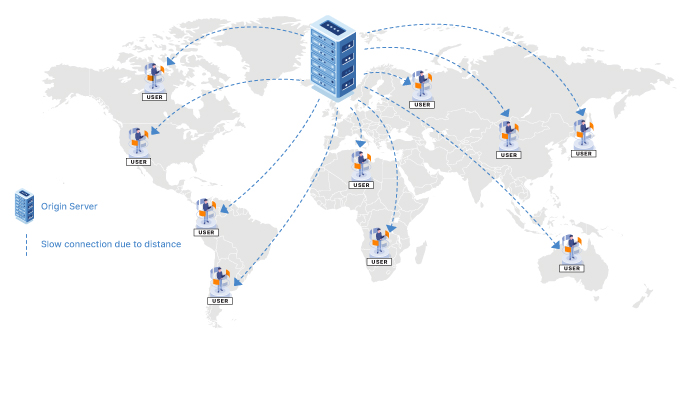
Content is served from the original location. This uses more processing power and bandwidth, taking longer to reach the user and resulting in increased load and an inferior user experience.
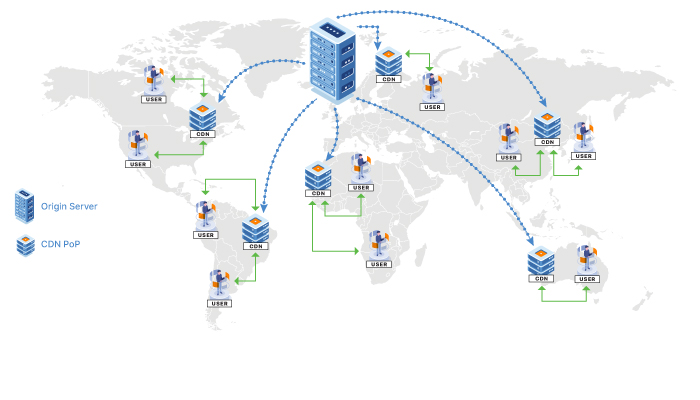
Content is mainly served from the closest CDN PoP server. Delivery from the cache server reduces load on your origin servers and provides content to the user faster, resulting in a superior user experience.